Create Actors#
Every object added to a SAPIEN Scene is an Entity. An Entity with
physical properties is commonly called an actor.
In this tutorial, you will learn the following:
Create
Entityand addComponentCreate rigid body actors using primitives (box, sphere, capsule)
Create rigid body actors using mesh files
Use
Poseto set the pose of an Entity
The full script can be downloaded here create_actors.py.
The collision and visual meshes of the banana are avilable at
collision.obj and visual.glb
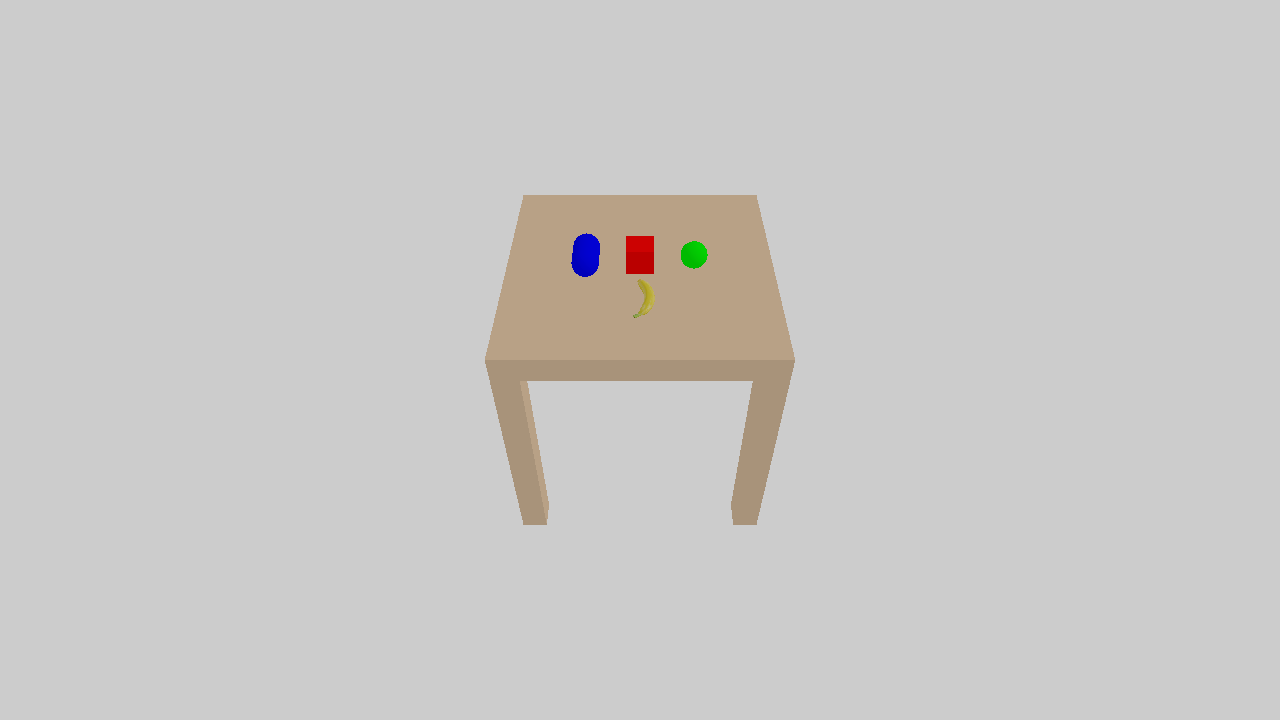
Create an Entity#
The only properties of an Entity include a pose (position and rotation) and
a name. The behavior of an Entity is completely determined by its attached
components. A PhysxRigidDynamicComponent makes the entity follow rigid body
dynamics in the PhysX simulator. A RenderBodyComponent allows this entity to
be rendered by cameras.
The following code shows how we create an Entity, set its pose and name, attach a physical component and a render component, and add it to the scene.
def create_box(
scene: sapien.Scene,
pose: sapien.Pose,
half_size,
color=None,
name="",
) -> sapien.Entity:
"""Create a box.
Args:
scene: sapien.Scene to create a box.
pose: 6D pose of the box.
half_size: [3], half size along x, y, z axes.
color: [4], rgba
name: name of the actor.
Returns:
sapien.Entity
"""
entity = sapien.Entity()
entity.set_name(name)
entity.set_pose(pose)
# create PhysX dynamic rigid body
rigid_component = sapien.physx.PhysxRigidDynamicComponent()
rigid_component.attach(
sapien.physx.PhysxCollisionShapeBox(
half_size=half_size, material=sapien.physx.get_default_material()
)
)
# create render body for visualization
render_component = sapien.render.RenderBodyComponent()
render_component.attach(
# add a box visual shape with given size and rendering material
sapien.render.RenderShapeBox(
half_size, sapien.render.RenderMaterial(base_color=[*color[:3], 1])
)
)
entity.add_component(rigid_component)
entity.add_component(render_component)
entity.set_pose(pose)
# in general, entity should only be added to scene after it is fully built
scene.add_entity(entity)
# name and pose may be changed after added to scene
# entity.set_name(name)
# entity.set_pose(pose)
return entity
Note
Collision shapes do not necessarily correspond to visual shapes. For example, you might have a simple collision shape for fast simulation, but a complicated visual shape for realistic rendering.
The pose of the box in the world frame can be specified by Pose. Pose
describes a 6D pose, consisting of a 3-dim position vector p and a 4-dim
quaternion q (to represent the rotation, in the wxyz convention).
Create an actor with ActorBuilder#
Creating an actor with the low-level entity API seems a bit tedious, so we
provide a convenience class ActorBuilder intended for building actors. The
same box can be create with the following code.
def create_box_v2(
scene: sapien.Scene,
pose: sapien.Pose,
half_size,
color=None,
name="",
) -> sapien.Entity:
"""Create a box.
Args:
scene: sapien.Scene to create a box.
pose: 6D pose of the box.
half_size: [3], half size along x, y, z axes.
color: [3] or [4], rgb or rgba
name: name of the actor.
Returns:
sapien.Entity
"""
half_size = np.array(half_size)
builder: sapien.ActorBuilder = scene.create_actor_builder()
builder.add_box_collision(half_size=half_size) # Add collision shape
builder.add_box_visual(half_size=half_size, material=color) # Add visual shape
box: sapien.Entity = builder.build(name=name)
box.set_pose(pose)
return box
Apart from box, the primitive shapes supported by SAPIEN also include sphere, capsule and cylinder. Example code for creating sphere and capsule are included in the code. A cylinder is a special primitive, since a cylinder collision primitive is not natively supported by PhysX. We implement cylinder collision with a convex mesh.
Create an actor with multiple primitives#
Next, we show an example to create an actor (table) by multiple boxes (a tabletop with four legs).
def create_table(
scene: sapien.Scene,
pose: sapien.Pose,
size,
height,
thickness=0.1,
color=(0.8, 0.6, 0.4),
name="table",
) -> sapien.Entity:
"""Create a table (a collection of collision and visual shapes)."""
builder = scene.create_actor_builder()
# Tabletop
tabletop_pose = sapien.Pose(
[0.0, 0.0, -thickness / 2]
) # Make the top surface's z equal to 0
tabletop_half_size = [size / 2, size / 2, thickness / 2]
builder.add_box_collision(pose=tabletop_pose, half_size=tabletop_half_size)
builder.add_box_visual(
pose=tabletop_pose, half_size=tabletop_half_size, material=color
)
# Table legs (x4)
for i in [-1, 1]:
for j in [-1, 1]:
x = i * (size - thickness) / 2
y = j * (size - thickness) / 2
table_leg_pose = sapien.Pose([x, y, -height / 2])
table_leg_half_size = [thickness / 2, thickness / 2, height / 2]
builder.add_box_collision(
pose=table_leg_pose, half_size=table_leg_half_size
)
builder.add_box_visual(
pose=table_leg_pose, half_size=table_leg_half_size, material=color
)
table = builder.build(name=name)
table.set_pose(pose)
return table
We can call add_box_collision(pose=Pose(...), ...) to set the pose of a collision shape in the actor frame.
Similarly, we can call add_box_visual(pose=Pose(...), ...) for a visual shape.
Note that table.set_pose(pose) sets the pose of the actor in the world frame.
Create an actor from a mesh file#
Apart from primitives, actors can also be created from mesh files.
builder = scene.create_actor_builder()
builder.add_convex_collision_from_file(
filename="../assets/banana/collision_meshes/collision.obj"
)
builder.add_visual_from_file(filename="../assets/banana/visual_meshes/visual.glb")
mesh = builder.build(name="mesh")
mesh.set_pose(sapien.Pose(p=[-0.2, 0, 1.0 + 0.05]))
Note
Any collision shape for dynamic rigid bodies in SAPIEN is required to be convex. To this end, a mesh will be “cooked” into a convex mesh before being used in the simulation.
Remove an entity#
After entity is added to the scene, either manually or added by an actor
builder, you can call scene.remove_entity(entity) or
entity.remove_from_scene() to remove it. A removed entity could be added to
a scene again, but an entity already in a scene may not be added again.