Physics#
Since SAPIEN is a physical simulation framework, we would like to showcase how to change physical properties which lead to different behaviors.
In this tutorial, you will learn the following:
Use
PhysxSceneConfigto initialize default physical propertiesUse
PhysxMaterialto set different physical materialsCreate kinematic actors
Enable damping for actors
Get kinematic quantities (pose, velocity, angular velocity) of an rigid body
The example illustrates an object sliding down the slope.
You can run the script with different arguments.
transforms3d is required to compute poses, which can be installed by pip install transforms3d.
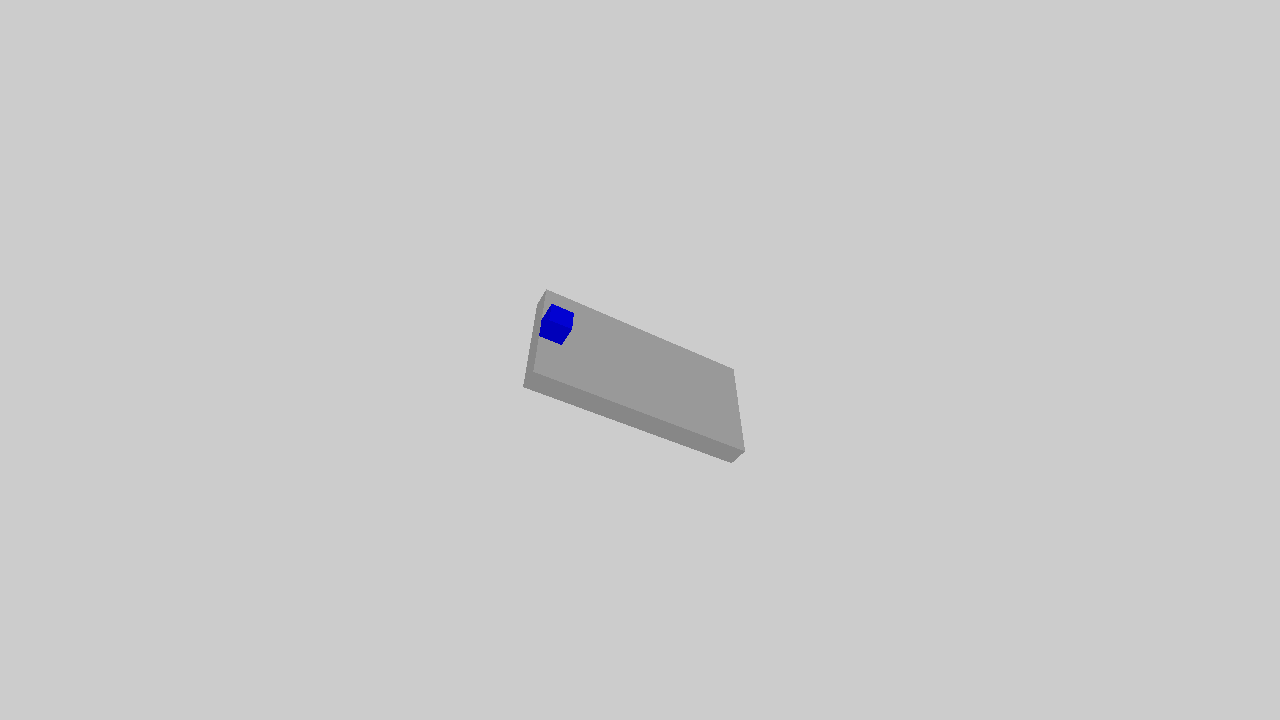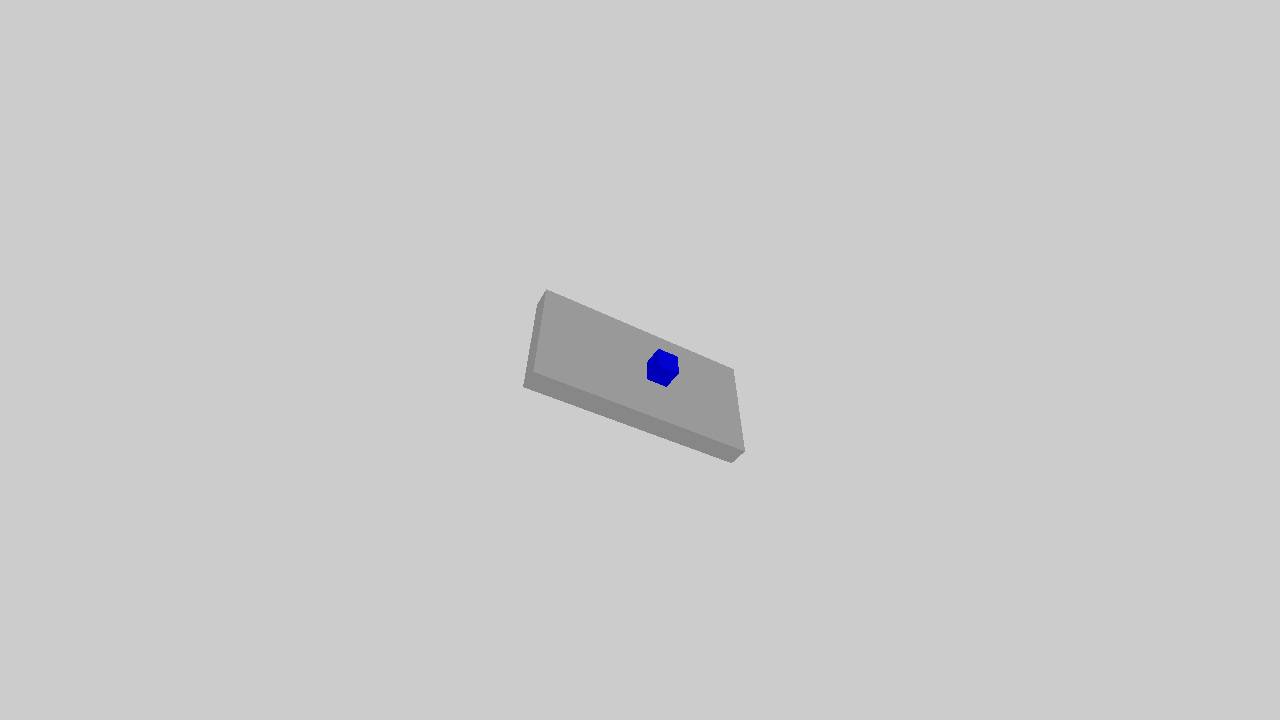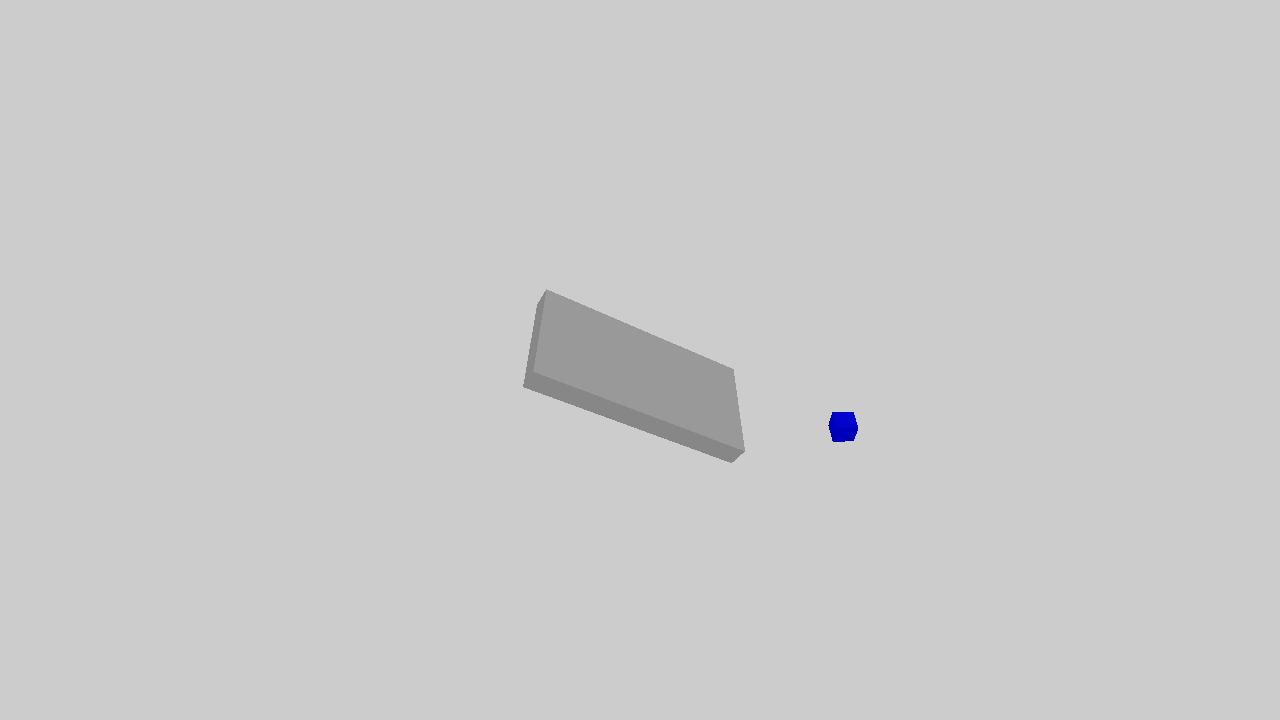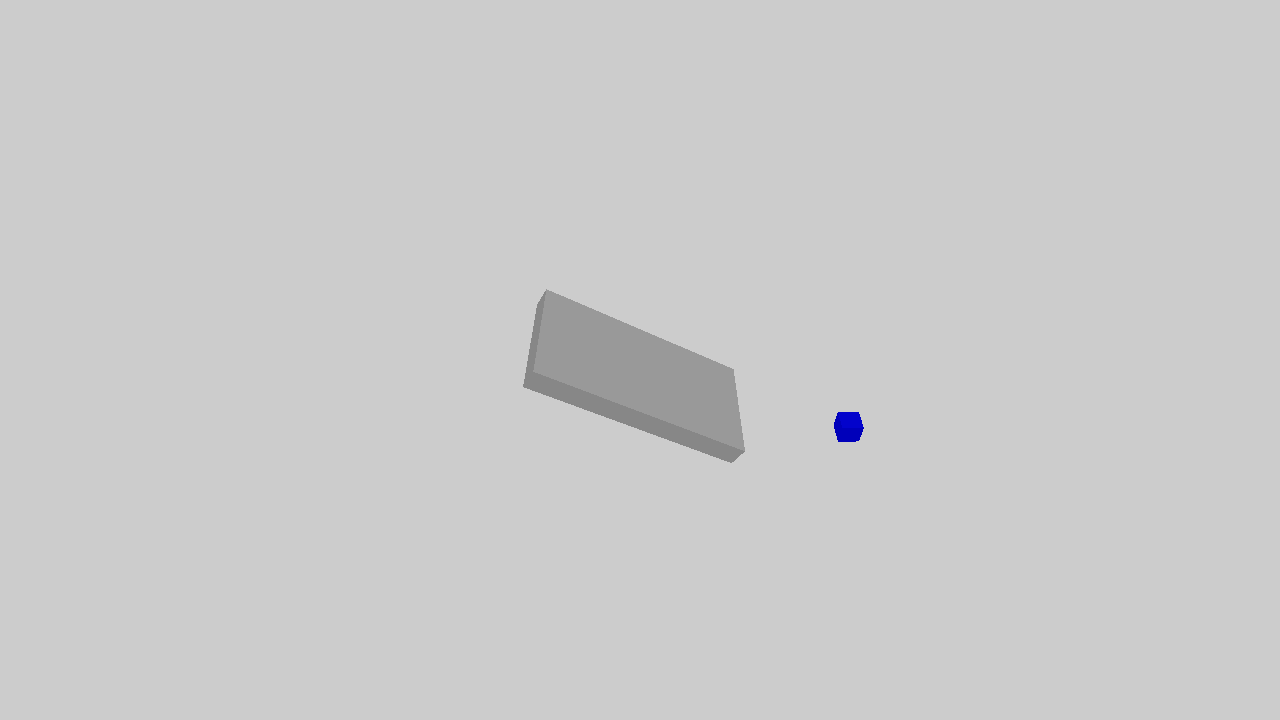
The full script can be downloaded here physics.py
Set default physical properties#
Default physical properties can be specified when a scene is created. Those properties include gravity, static and dynamic friction, as well as restitution (elasticity of collision).
scene_config = sapien.physx.PhysxSceneConfig()
# The default physical properties can be modified through sapien.SceneConfig
print(scene_config.gravity)
scene_config.gravity = np.array([0.0, 0.0, args.gravity])
sapien.physx.set_scene_config(scene_config)
# SAPIEN's default physical material for PhysX can be modified at any time
# It is not bound to a scene
default_material = sapien.physx.get_default_material()
print(default_material.static_friction)
print(default_material.dynamic_friction)
print(default_material.restitution)
sapien.physx.set_default_material(
static_friction=0.3, dynamic_friction=0.3, restitution=0.0)
# by default, SAPIEN scene consists of PhysxSystem and RenderSystem
# The PhysxSystem can take a PhysxSceneConfig to custom its behavior
scene = sapien.Scene([
sapien.physx.PhysxCpuSystem(),
sapien.render.RenderSystem(),
Note PhysxSceneConfig describes physical properties global to a scene. However, the default physical material is global to the entire SAPIEN process.
Set physical materials#
PhysxMaterial describes physical (contact) properties (friction and restitution) of the material of an PhysX rigid body.
It can be specified in the ActorBuilder when an actor is created.
If not provided, the default physical material, induced by the scene’s default physical properties, will be used.
# It is not bound to a scene
default_material = sapien.physx.get_default_material()
print(default_material.static_friction)
print(default_material.dynamic_friction)
print(default_material.restitution)
sapien.physx.set_default_material(
Some other physical properties, like density, are directly provided to collision shapes. We update create_sphere function in Create Actors.
def create_sphere(
scene: sapien.Scene,
pose: sapien.Pose,
radius,
color=None,
density=1000.0,
physical_material: sapien.physx.PhysxMaterial = None,
name='',
) -> sapien.Entity:
"""Create a sphere."""
builder = scene.create_actor_builder()
builder.add_sphere_collision(radius=radius, material=physical_material, density=density)
builder.add_sphere_visual(radius=radius, material=color)
sphere = builder.build(name=name)
sphere.set_pose(pose)
return sphere
Note
The rolling resistance (friction) is not modeled currently in SAPIEN.
Create a kinematic actor#
Now, let’s create a slope.
The slope should be a kinematic object, rather than a dynamic object.
In other words, it can not be affected by external forces.
We can set is_kinematic=True when building the actor.
def create_box(
scene: sapien.Scene,
pose: sapien.Pose,
half_size,
color=None,
is_kinematic=False,
density=1000.0,
physical_material: sapien.physx.PhysxMaterial = None,
name='',
) -> sapien.Entity:
"""Create a box.
Args:
scene: sapien.Scene to create a box.
pose: 6D pose of the box.
half_size: [3], half size along x, y, z axes.
color: [3] or [4], rgb or rgba.
is_kinematic: whether an object is kinematic (can not be affected by forces).
density: float, the density of the box.
physical_material: physical material of the actor.
name: name of the actor.
Returns:
sapien.Entity
"""
half_size = np.array(half_size)
builder = scene.create_actor_builder()
builder.add_box_collision(half_size=half_size, material=physical_material, density=density) # Add collision shape
builder.add_box_visual(half_size=half_size, material=color) # Add visual shape
if is_kinematic:
box = builder.build_kinematic(name=name)
else:
box = builder.build(name=name)
box.set_pose(pose)
return box
Set damping for the actor#
Sometimes, you might model some resistance proportional to (linear or angular) velocity, like air resistance. It can be achieved by setting the damping of an actor.
rigid_component = actor.find_component_by_type(sapien.physx.PhysxRigidBodyComponent)
rigid_component.set_linear_damping(args.linear_damping)
Get kinematic quantities (pose, velocity) of an actor#
We can acquire kinematic quantities (pose, linear velocity, angular velocity) of an actor through get_pose(), get_linear_velocity(), get_angular_velocity().
print('step:', steps)
print('Pose', actor.get_pose())
print('Velocity', rigid_component.get_linear_velocity())